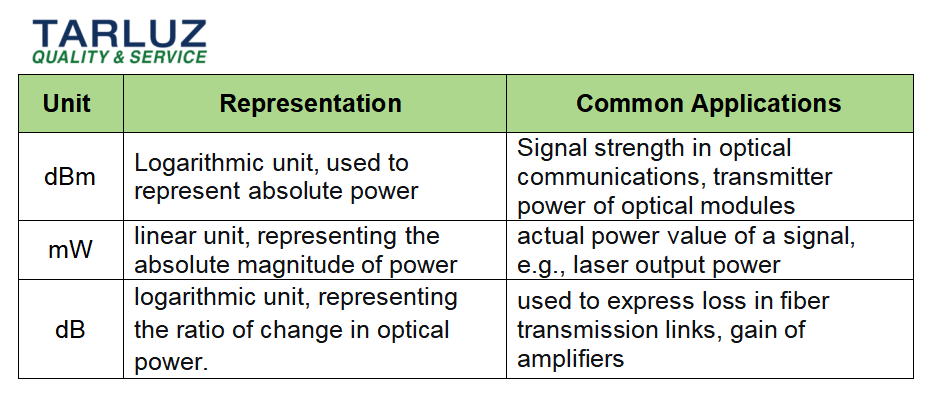
In the field of optical communications, dBm, mW, and dB are three commonly used units. Understanding the relationship between them can help engineers make more precise judgments when designing and optimizing optical communication systems. This article briefly introduces the definitions and interrelationships of these three.
Relationship between dBm and mW
dBm (decibel-milliwatt) and mW (milliwatt) are both common units for optical power. dBm is a logarithmic unit representing the power level relative to 1 milliwatt. It compresses a wide power range into manageable numbers through logarithmic operations. In contrast, mW is a linear unit representing the actual value of power.
The conversion relationship between them is as follows:
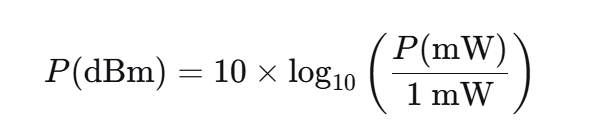
Where P is the optical power in mW.
To convert from dBm to mW, we use the following formula:
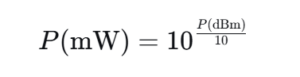
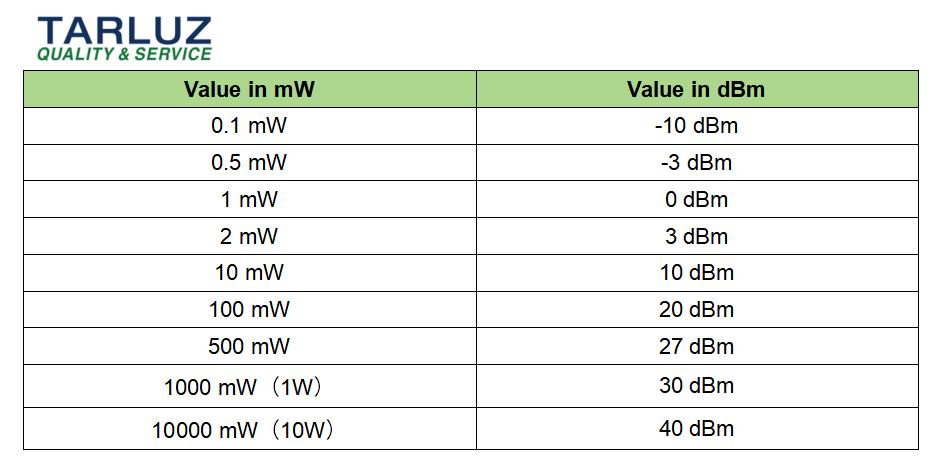
Comparison Table of Common Optical Powers Expressed in mW and dBm
Relationship between dB and dBm
dB (decibel) is a relative unit used to express the ratio between two optical powers. It does not depend on absolute power values but is used to indicate the gain or attenuation of optical power.
For example, given two optical powers, P1 and P2, their difference can be expressed in dB:
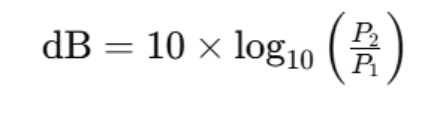
That is: dB = 10 x lgP2 — 10 x lgP1 = dBm2 — dBm1.
If optical power is expressed in dBm, then dB is the difference between the optical power values. When expressing the insertion loss of an optical component, we only need to subtract the dBm values of the input and output optical powers.
Comparative Analysis of dBm, mW, and dB