As data centers continuously evolve towards higher bandwidth and larger scale, 800G optical modules have become critical infrastructure supporting AI computing, high-performance computing, and cloud services. Their importance lies not only in the leap in transmission rates but also in the significant improvement in data exchange efficiency and density through technological integration, reducing per-bit power consumption and cost, thereby providing core interconnect capabilities for next-generation data centers. In this context, rational cabling strategies are crucial for fully leveraging 800G performance.
800G and 400G – Server to Switch Applications
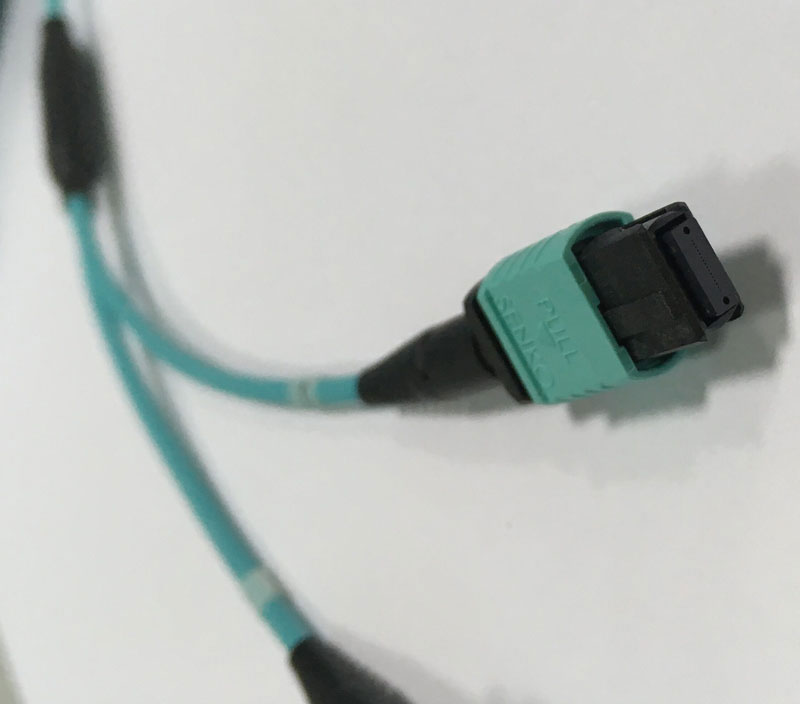
Using Point-to-Point Cabling Connecting MPO-8/12 APC to MPO-8/12 APC
This scenario typically uses point-to-point cabling to connect servers and leaf switches within the same rack or cabinet. It offers a simple structure and low latency, making it suitable for short-distance, high-bandwidth connections. It can also be extended for links between different switch levels, such as leaf-spine or spine-core. However, if switches are located in different areas (e.g., separate rooms or distant rows), point-to-point cabling is not recommended due to increased fiber length, signal attenuation, and complexity. In such cases, a structured cabling system is preferred to ensure signal quality and ease of maintenance.
Application Scenario ①
An 800G dual-port OSFP optical module can be connected to a peer 800G dual-port OSFP optical module via 2 MPO-8/12 APC fiber jumpers.
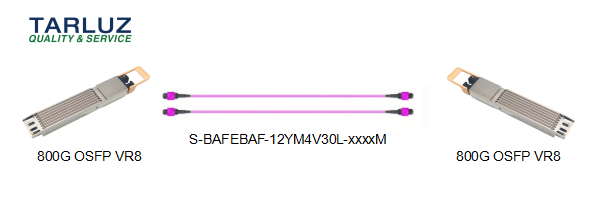
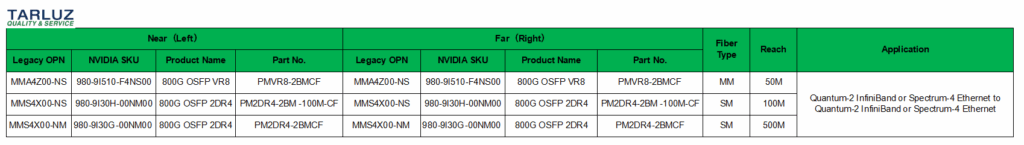
Application Scenario ① Compatible Optical Module Models
Application Scenario ②
An 800G dual-port OSFP optical module can be connected to a peer 400G dual-port OSFP optical module via 2 MPO-8/12 APC fiber jumpers. (Using only 1 out of the 2 ports)
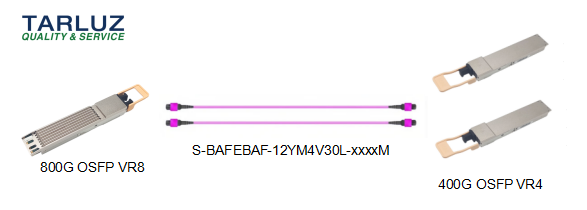
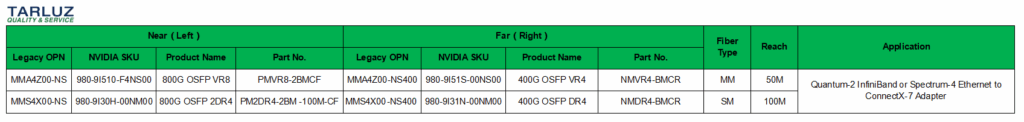
Application Scenario ② Compatible Optical Module Models
Application Scenario ③
An 800G dual-port OSFP optical module can be connected to a peer 400G single-port QSFP112 optical module via 2 MPO-8/12 APC fiber jumpers.

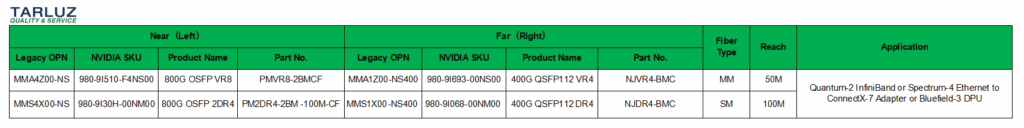
Application Scenario ③ Compatible Optical Module Models

