The Octal Small Form Factor Pluggable (OSFP) module, widely adopted for high-speed optical interconnects, is available in three primary structural forms that address different thermal and mechanical requirements: Closed Top, Finned Top, and Riding Heatsink (RHS).
Finned Top Heatsink (Open Top Heatsink)
In contrast, the finned top design exposes heatsink fins on the upper surface. This structure enhances airflow and improves thermal dissipation for higher-power modules. However, it requires strict compliance with dimensional rules to protect EMI contacts and maintain shielding. The fin geometry also allows additional airflow channels, making it suitable for next-generation power-intensive optics. 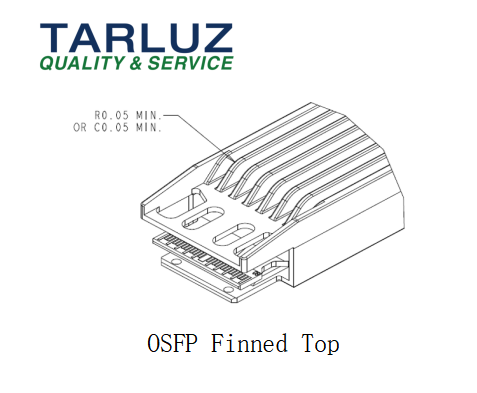
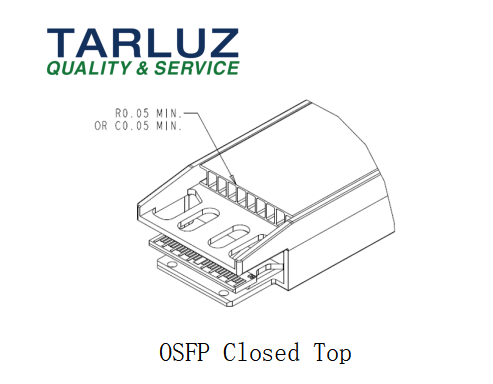
Closed Top Heatsink
The closed top OSFP integrates a solid heatsink on its upper surface, ensuring mechanical rigidity and reliable EMI shielding. Airflow is directed along the module length, and its smooth trailing edge design prevents mechanical interference with riding heatsinks. This configuration is common for standard power modules and provides balanced thermal performance.
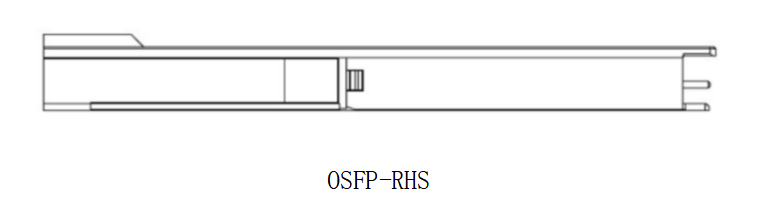
OSFP-RHS (Riding Heatsink)
The OSFP-RHS module differs significantly by removing the integrated heatsink entirely. Instead, cooling is achieved through an external riding heatsink mounted on the cage. With a 9.5 mm profile and a shifted forward stop to prevent mis-mating, OSFP-RHS is designed for advanced cooling solutions, including stacked cages and liquid-cooled systems. This architecture offers maximum flexibility for thermal management in dense, high-power networking equipment.
Together, these three OSFP module structures provide manufacturers and system designers with flexible solutions to balance thermal performance, EMI compliance, and mechanical integration across diverse deployment scenarios.